Electricity has become an essential part of every field of life and production. One of the most important devices in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is the dynamo generator. Although it was invented a long time ago, the dynamo generator still plays a vital role in many modern electrical systems, especially where direct current (DC) is required. This article will help you better understand the structure, operating principle, and practical applications of the dynamo generator.
Contents
Structure and working principle of a dynamo generator
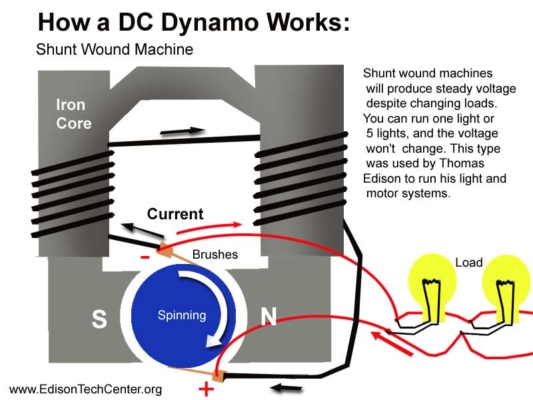
Basic Components of a Dynamo Generator
A dynamo generator is a type of direct current (DC) generator that operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. A typical dynamo consists of the following main components:
Rotor (Armature): The rotating part connected to the shaft that spins inside the magnetic field. As it rotates, it changes the magnetic flux through the coil and generates electricity.
Stator (Field system): The stationary part that provides the magnetic field. This field can be created using permanent magnets or electromagnetic field windings.
Armature winding: The wire coils inside the rotor where electricity is generated by electromagnetic induction.
Commutator: A key feature of a dynamo generator. It acts as a mechanical rectifier, converting alternating current (AC) generated in the armature winding into direct current (DC) output.
Carbon brushes: These make contact with the commutator and allow current to pass from the rotating part to the external circuit. Although they wear out over time, brushes are essential for maintaining electrical continuity.
The coordinated operation of these components enables the dynamo generator to produce a stable DC output for a wide range of applications.
Operating Principle of a Dynamo Generator
The dynamo generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831. According to this principle, when a conductor (such as a coil) moves through a magnetic field—or when the magnetic field around it changes—an electromotive force (EMF) is induced, generating electric current.
In a dynamo, as the rotor spins within the stator’s magnetic field, the magnetic flux through the armature windings constantly changes. This change in flux induces an EMF in the coil. Initially, the induced current is alternating in nature. However, the commutator acts as a mechanical rectifier that, together with the brushes, ensures that the output current is unidirectional (DC).
The output voltage of the dynamo is directly affected by the rotor’s speed and the strength of the magnetic field. Higher speeds or stronger fields result in higher voltage. Therefore, systems using dynamo generators may include speed regulators or field current controllers to stabilize the output voltage.
Applications and benefits of dynamo generators in daily life and industry
Real-World Applications of Dynamo Generators
Despite the rise of more modern generators like alternators, the dynamo generator still serves important roles, especially in systems that require a stable DC power source:
Bicycles: Perhaps the most common civilian use. Dynamos mounted on bike wheels generate electricity to power lights while the bike is in motion.
Early automobiles: Before alternators became standard, older cars used dynamo generators to charge batteries and power lighting and ignition systems.
Industrial use: In control systems, DC motor drives, conveyor belts, older CNC lathes, and battery-based systems, dynamos are used where stable DC is required.
Renewable energy: Small-scale wind or hydroelectric systems in remote areas often use dynamo generators because they are low-cost and easy to maintain.
Military and specialized equipment: Certain military devices, geological instruments, and field survey tools still rely on dynamo generators for independent power in extreme environments.
See more:Why are Italia alternator becoming increasingly popular in Vietnam?
See more: Dynamo is Rotating DC Alternators in Electrical Engineering
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dynamo Generators
Although it’s an older technology, the dynamo generator has several noteworthy advantages that make it viable in certain scenarios.
Advantages:
Simple design: The structure is not complex, making dynamos easy to manufacture, repair, and maintain.
Efficient at low loads: Dynamos operate efficiently in systems with small or variable loads.
Direct DC output: Ideal for applications that require DC, such as battery charging or DC motor control.
Disadvantages:
Mechanical wear: The use of brushes and commutators leads to mechanical wear, reducing efficiency over time and requiring regular maintenance.
Limited power capacity: Not suitable for high-power systems or applications that need a large, stable current.
Less stable than alternators: Unlike alternators that use diodes for rectification, dynamos rely on mechanical components, which can cause sparks and wear, leading to reduced lifespan and stability.
However, for DC applications that require low cost, easy maintenance, and independence from the grid, the dynamo generator remains a practical solution.
Understanding the structure, operating principles, and applications of the dynamo generator not only helps maximize its use but also opens creative avenues for harvesting mechanical energy to generate electricity—especially in remote or off-grid systems.
Additional knowledge about dynamo generator
Beyond practical applications, the dynamo generator plays a vital role in education and electrical engineering research. Many universities and vocational training centers use dynamos as hands-on tools to demonstrate electromagnetic induction, machine structure, and energy conversion. Due to its simplicity, students can easily disassemble and reassemble the machine, gaining valuable real-world experience.
In the DIY (do-it-yourself) and maker communities, the dynamo is also a favorite. Tinkerers and community projects in remote regions often repurpose dynamos from bicycles or small motors to build lighting systems, ventilation fans, or phone chargers. Its ability to generate electricity instantly from mechanical motion makes it perfect for low-cost, off-grid setups.
In the context of eco-friendly living and energy-saving, dynamo generators are increasingly used in green products. Examples include hand-crank flashlights, emergency radios, or mobile phone chargers—all powered by dynamo generators. These devices are especially useful for outdoor activities, expeditions, or during natural disasters when conventional power sources are unavailable.
Its flexibility, simplicity, and accessibility make the dynamo generator a continuing presence in both traditional and modern technology. By combining old-school mechanics with new-age creativity, the dynamo maintains its relevance in today’s electric world.
| Main Topic | Summary |
| Definition | A dynamo generator is a DC generator that uses electromagnetic induction to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. |
| Key Components | Rotor, stator, armature winding, commutator, and carbon brushes. |
| Working Principle | Based on Faraday’s law: rotating coils in a magnetic field induce voltage; the commutator converts AC to DC. |
| Applications | Used in bicycles, old vehicles, industry, renewable energy, military gear, and emergency equipment. |
| Advantages | Simple design, easy maintenance, efficient for low loads, provides direct DC output. |
| Disadvantages | Mechanical wear from brushes and commutator, limited power capacity, less stable than alternators. |
| Educational Use | Common in teaching, DIY projects, and green energy tools like hand-crank chargers and radios. |
Company name:
TTTT GLOBAL co Ltd,.
- Address: Landmark 4 Building, Vinhomes Central Park, 720A Dien Bien Phu Str, Ward 22, Binh Thanh District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
- Website: https://ttttglobal.com/en/
- Hotline: +84286 2728 334
- Email: Info@ttttglobal.com





![Collection of genuine Volvo Penta TAD841GE PDF engine technical documents [Free download] General introduction to TAD841GE engine](https://ttttglobal.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/tad841ge-pdf-2.jpg)